A key element of being a specialist in medical practice is the ability to teach and support in a formal setting and in the workplace. It is a GMC requirement that all those training to UK Royal College curricula develop such skills. This includes being able to set learning objectives and deliver a teaching session, deliver effective feedback, undertake training and supervision in the clinical environment and understand the principles to mentor and appraise other members of the EM clinical team and workforce.
Domain 1: Professional values and behaviours
Domain 8: Capabilities in education and training
Key ACCS capabilities
At completion of ACCS a trainee:
- Will be able to set learning objectives for and deliver a teaching session
- Will be able to deliver effective feedback to a junior colleague or allied health professional with an action plan
Key EM capabilities
At completion of Intermediate training a trainee will be able to
- set learning objectives for and deliver a teaching session that demonstrates growing expertise from ACCS
- deliver effective feedback to a junior colleague or allied health professional
At completion of higher training a trainee will:
- be able to undertake training and supervision of members of the ED team in the clinical environment
- be able to prepare and deliver teaching sessions outside of the clinical environment; including simulation, small-group work and didactic teaching
- be able to provide effective constructive feedback to colleagues, including debrief
- understand the principles necessary to mentor and appraise junior doctors
- Delivers effective teaching and training to medical students, junior doctors and other health care professionals
- Delivers effective feedback with action plan
- Able to supervise less experienced trainees in their clinical assessment and management of patients
- Able to supervise less experienced trainees in carrying out appropriate practical procedures
- Able to act a clinical supervisor to doctors in earlier stages of training
RCEMLearning is the primary RCEM resource for trainees and trainers developing skills in teaching and supervision
The RCEMLearning website reflects the 2021 Curriculum specialty learning outcomes and includes a section dedicated to SLO 9.
There is also a wealth of other medical education resources and opportunities available including:
- Generic Instructors Course and ATLS Instructors course
- Train the trainers courses
- NHS e-learning for healthcare – Educator Training Resources
- Local undergraduate teaching – formal and informal
- Postgraduate and multidisciplinary education – formal and informal teaching, supervision and support
- Local opportunities with departments of medical education, undergraduate medical courses and postgraduate deaneries
Details and links can be found in the Resources section of this SLO.
Postgraduate Doctors training in Emergency Medicine should be involved throughout their training programme in local undergraduate, postgraduate and multidisciplinary educational activities – from formal teaching to informal teaching, supervision and support in the workplace.
Two of the educational principles that have been considered in developing EM capabilities have been ‘spacing’ and ‘Interleaving’. These terms mean that there is likely to be better retention of knowledge and integration of curriculum elements if they are introduced early and revisited for reinforcement, and if the layering of greater complexity is interspersed with other curricular content.
The GMC require all curricula to include the ability to teach and educate in all stages of training, this being one of their Generic Professional Capabilities. The development and application of teaching skills starts in ACCS and builds throughout training with development of supervision and feedback skills being the focus of intermediate and higher training.
Teaching and supervision are within the Programme of Learning at all stages of training, and the requirements of the curriculum reflect growing expertise and responsibility in this subject over time.
How is this SLO assessed?
Assessment in the workplace
Trainees at all stages are expected to demonstrate some activity in this SLO in each year of training. It is recognised that the extent of this may vary to a degree year-by-year according to trainees’ activity against the other generic SLOs. By the end of training trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for all four HST Key Capabilities.
All activity relating to teaching is relevant and the list of evidence that might be used is not reductive in any way. Some trainees may be inspired by the topic and seek to stretch further in this area. The following tools and opportunities, are available to gain formative feedback on the Key Capabilities of this SLO:
The Structured Teaching Assessment Tool (STAT)
The assessment schedule has an expectation that trainees develop their teaching throughout their training and expects that teaching should be viewed as a core part of the requirements of the emergency physician. The STAT is available on the ePortfolio to guide trainees through such an exercise and for this to be reviewed by their clinical or educational supervisor. The tool can be used for both face-to-face and online teaching and is adaptable to all types of teaching episode.
Extended Supervised Learning Episode (ESLE)
Supervisors conducting an ELSE for a trainee are likely to observe the trainee undertaking workplace supervision and feedback for colleagues as part of the overall episode. This evidence can be recorded by the supervisor when completing the ELSE form.
Multi-Source Feedback (MSF)
Teaching and supervision are an important domain of the MSF that provides valuable feedback to the trainee and which can be reviewed by their clinical and/or educational supervisor.
Structured feedback from external teaching opportunities
During training there may be many opportunities to teach beyond the local environment. Examples include courses (e.g. ALS, APLS, ATLS, ETC), conference workshops, university teaching and teaching of other medical specialties and the wider multidisciplinary team. Structured feedback from such episodes provides valuable evidence to be added to the e-portfolio.
Educational review
Summative assessment each year is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the ACCS ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. By the end of the two years of ACCS training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the key capability of this SLO.
Standard required
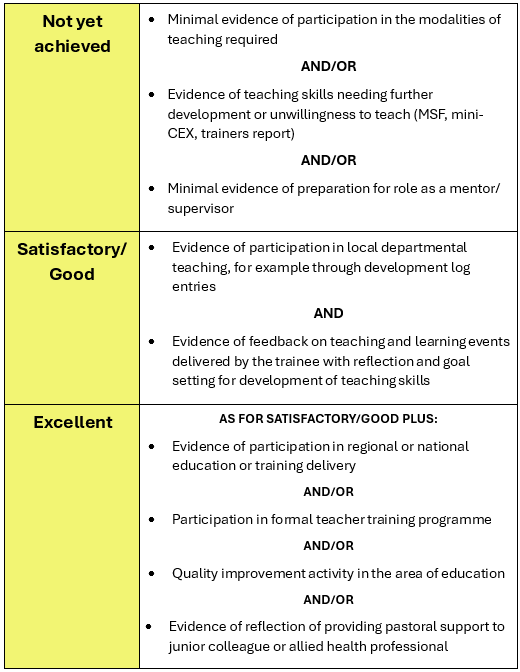
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
End of ACCS:
Educational review
Summative assessment at the end of intermediate training is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the Intermediate ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. By the end of intermediate training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the two key capabilities of this SLO.
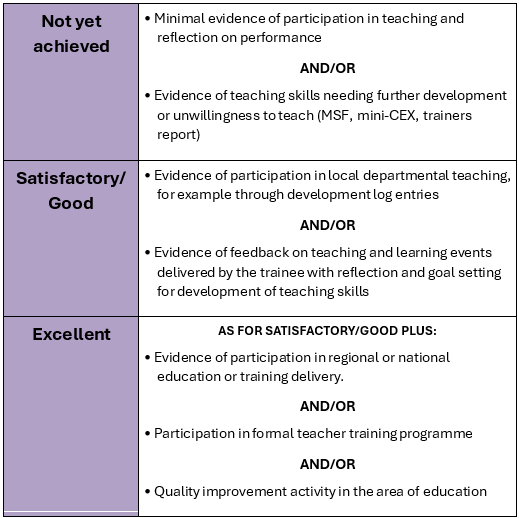
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
End of Intermediate:
Educational review
Summative assessment in each year of higher training is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the Higher ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. There is a requirement for progression year on year towards the elements described. It is possible to progress through these more rapidly if trainees have a particular interest or opportunities in this SLO. By the end of higher training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the four key capabilities of this SLO.
RCEM examinations
The content of this SLO is also assessed in the formal examination schedule.
FRCEM OSCE
In addition to assessing teaching of skills/knowledge the FRCEM OSCE also assesses the supervision of the team in the emergency department and the skills required to give appropriate feedback when asked for advice.
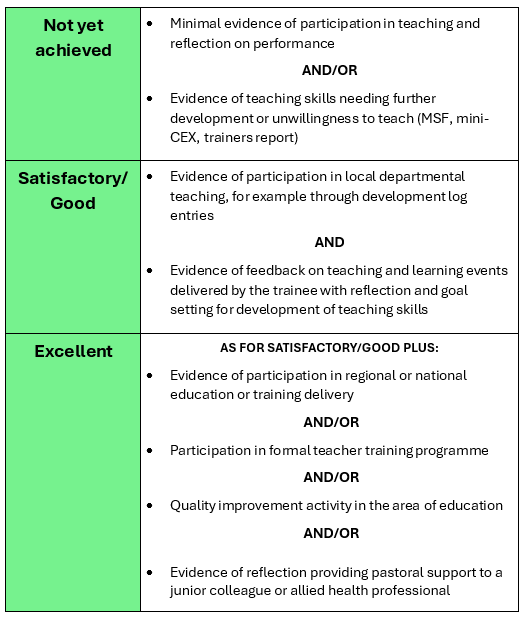
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
End of Higher: