A key element of being a specialist in medical practice is the ability to use research evidence to drive improvement in patient care. It is a GMC requirement that all those training to UK Royal College curricula develop such skills. It is no less important for those in Emergency Medicine, often a pragmatic and practical pursuit, but one in which it is fundamentally important that its clinical leaders can negotiate and utilise evidence to advocate for their unique patient group.
GPC Domains:
Domain 3: Professional knowledge
- professional requirements
- national legislative requirements
- the health service and healthcare systems in the four countries
Domain 9: Capabilities in research and scholarship
Key ACCS capabilities
At completion of ACCS a trainee will:
- be able to search the medical literature effectively and know how to critically appraise studies
Key EM capabilities
At completion of Intermediate training a trainee will:
- be able to appraise, synthesise and communicate research evidence
At completion of Higher training a trainee will:
- be able to appraise, synthesise, communicate and use research evidence to develop EM care
- be able to actively participate in research
- Manages clinical information/data appropriately
- Understands principles of research and academic writing
- Demonstrates ability to carry out critical appraisal of the literature
- Understands the role of evidence in clinical practice and demonstrates shared decision making with patients
- Demonstrates appropriate knowledge of research methods, including qualitative and quantitative approaches in scientific enquiry
- Demonstrates appropriate knowledge of research principles and concepts and the translation of research into practice
- Follows guidelines on ethical conduct in research and consent for research
- Understands public health epidemiology and global health patterns
- Recognises potential of applied informatics, genomics, stratified risk and personalised medicine and seeks advice for patient benefit when appropriate
RCEMLearning is the primary RCEM resource providing material to access for trainees and trainers in developing capabilities in critical literature appraisal (CLA). The RCEMLearning website reflects the 2021 Curriculum specialty learning outcomes and includes a section dedicated to SLO 10 as well as New in EM research-focussed podcasts in the podcast section.
There is also a wealth of other research-related resources and opportunities available that can be found in the Resources section of this SLO.
Postgraduate Doctors training in Emergency Medicine should be involved throughout their training programme in critical literature appraisal as well as understanding and participating in aspects of research.
The Assessment Schedule for the RCEM curriculum has been developed to best meet its aims and objectives. Two of the educational principles that have been considered in developing EM capabilities have been ‘spacing’ and ‘Interleaving’. These terms mean that there is likely to be better retention of knowledge and integration if curricular elements are introduced early, returned to for reinforcement, and if the layering of greater complexity is interspersed with other curricular content.
The curriculum requires trainees to demonstrate the ability to appraise and apply evidence in all stages of training, this being one of their Generic Professional Capabilities. The development and application of CLA knowledge starts in ACCS and builds throughout training to completion.
In this SLO there is a requirement to demonstrate not only the ability to appraise the relevant medical literature, but to be able to synthesise evidence and to communicate key findings and their clinical impact. These, after all, are the reasons why a day one EM consultant needs such skills – to contribute effectively to patient care improvement in the ED.
How is this SLO assessed?
Assessment in the workplace
Trainees at all stages are expected to demonstrate some activity in this SLO in each year of training. It is recognised that the extent of this may vary to a degree year-by-year according to trainees’ activity against the other generic SLOs. By the end of training trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for both HST Key Capabilities.
All activity relating to research is relevant and the list of evidence that might be used is not reductive in any way. Some trainees may be inspired by the topic and seek to stretch further in this area. The following tools and opportunities, are available to gain formative feedback on the Key Capabilities of this SLO:
The Applied Critical Appraisal Form (ACAF)
The assessment schedule has an expectation that trainees develop the ability to consider their clinical work and identify questions that they would like to seek further evidence from the medical literature to help answer. These may come from clinical encounters in the workplace, or from workplace-based assessment discussions. The ACAF is available on the ePortfolio to guide trainees through such an exercise and for this to be reviewed by their clinical or educational supervisor
Presentation at a Journal Club (JCF)
One of the Key Capabilities for this SLO within intermediate and higher training is:
- …able to appraise, synthesise, communicate research evidence
There is a requirement for trainees to provide evidence in Intermediate and Higher Training of the presentation and communication of key themes and ideas. There are a number of ways in which it is possible to evidence this:
- Presentation of posters/papers at local, regional or national meeting
- Presenting research findings in departmental meetings also constitutes evidence for this SLO
- Journal club – online or face-to-face meeting
Feedback at journal club can be captured within the ePortfolio using the bespoke Journal Club Presentation Form (JCF).
Educational review
Summative assessment each year is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the ACCS ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. By the end of the two years of ACCS training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the key capability of this SLO.
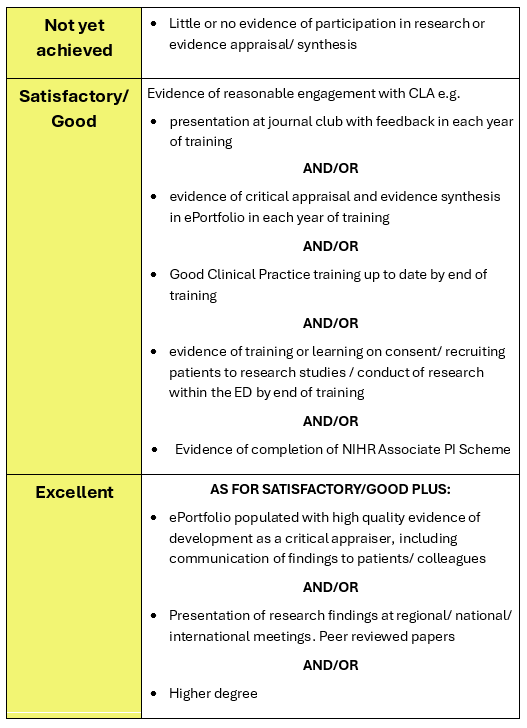
Standard required
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
End of ACCS:
Educational review
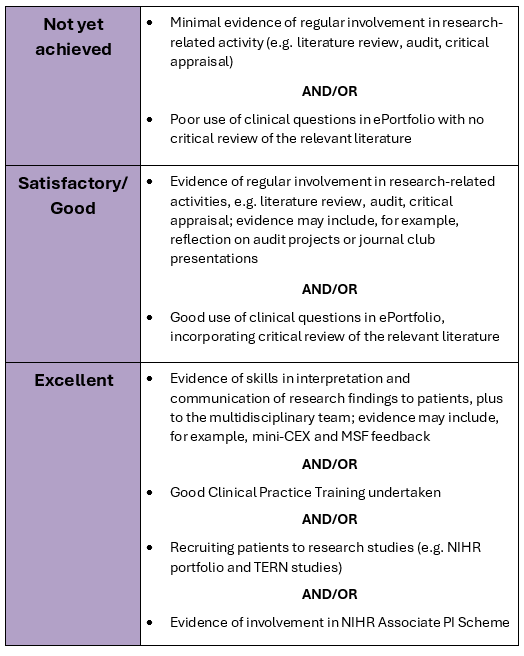
Summative assessment each year is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the Intermediate ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. By the end of intermediate training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the key capability of this SLO.
Standard required
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
Educational review
Summative assessment each year is a judgement by the Educational Supervisor and recorded on the Higher ESR form, with subsequent overview from the ARCP panel. By the end of the three years of higher training, trainees are required to provide sufficient evidence to at least a satisfactory standard for the two key capabilities of this SLO.
RCEM examinations
The content of this SLO is also assessed in the formal examination schedule.
FRCEM OSCE
In addition to the FRCEM OSCE also assesses the ability to appraise medical literature, to offer a defensible opinion on the application of research findings for clinical care, and to communicate research findings to patients or colleagues.
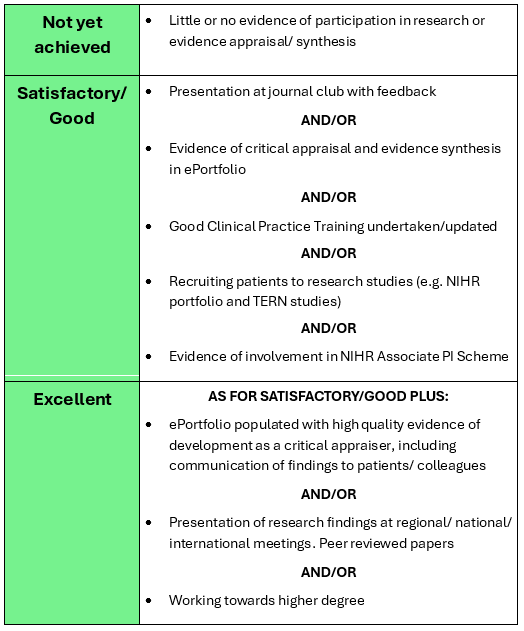
Standard required
The following table summarises the activity that is expected and how excellence might be pursued:
End of higher: